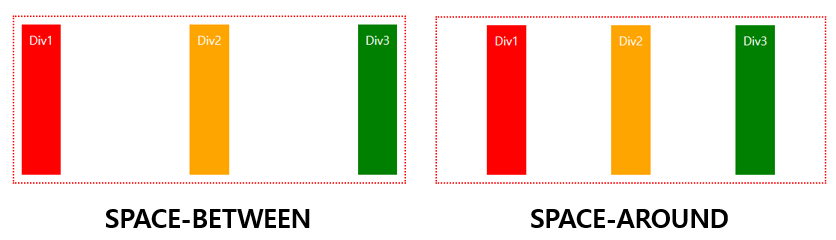
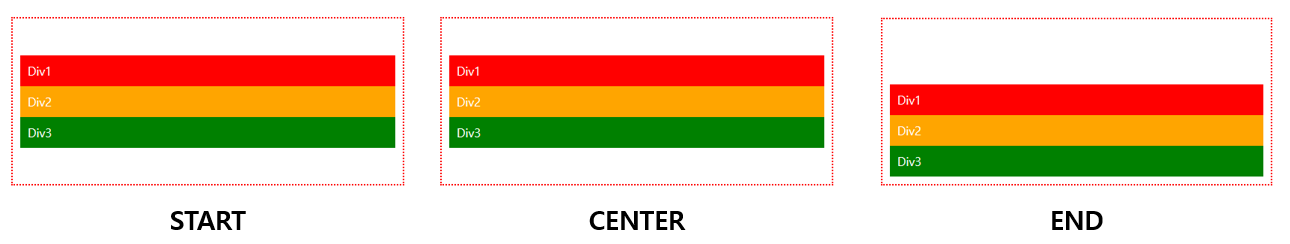
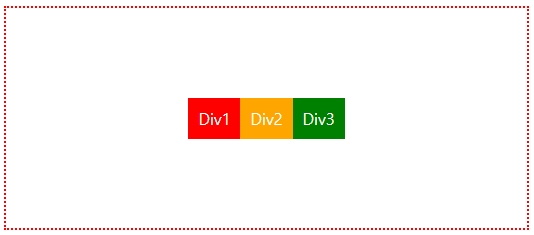
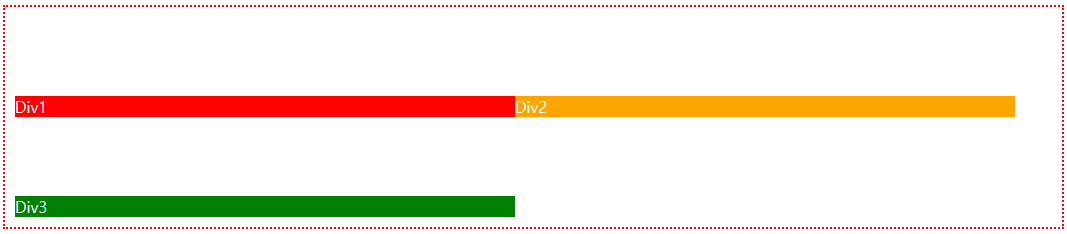
📝display:grid, grid-template-columns, grid-template-rows, gaps
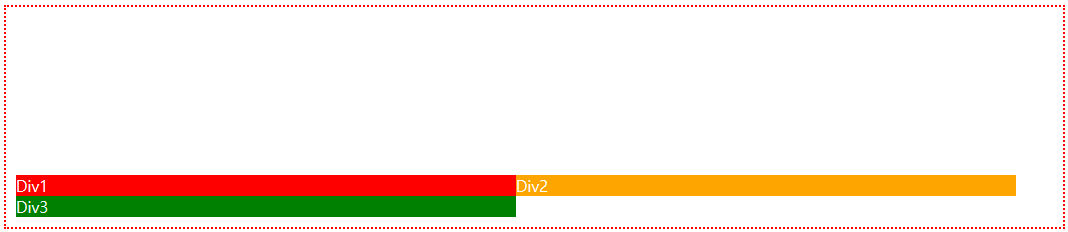
<div class="father">
<div class="child">1</div>
<div class="child">2</div>
<div class="child">3</div>
<div class="child">4</div>
</div>
.father {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 100px 200px 50px;
grid-template-rows: 200px 100px;
row-gap: 10px;
column-gap: 20px;
}
.child {
background-color: tomato;
display: flex;
color: white;
font-size: 28px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
Flexbox의 경우 1차원에 대한 배치와 정렬이면 Grid의 경우 2차원에 대한 배치와 정렬에 많이 쓰인다.
부모에 display:grid를 기본적으로 적용시켜야하고 grid-template-columns를 이용해 열의 가로 넓이를 지정하며 grid-template-rows를 이용해 행의 세로 넓이를 지정한다.
gap의 경우는 자식 div의 margin을 의미한다. (row-gap, column-gap으로 개별로 지정도 가능)
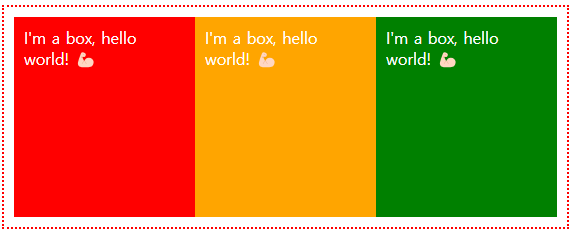
<div class="father">
<div class="child">1</div>
<div class="child">2</div>
<div class="child">3</div>
<div class="child">4</div>
</div>
.father {
display: grid;
grid-template-rows: 1fr 2fr 1fr;
grid-template-columns: 3fr 1fr;
// grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr);
// grid-template-rows: repeat(2, 1fr);
row-gap: 10px;
column-gap: 20px;
}
.child {
background-color: tomato;
display: flex;
color: white;
font-size: 28px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
만약 비율로 설정이 필요하면 fr로 설정하면 됩니다. 또한 동일한 경우 repeate로 간단하게 표현도 가능합니다.
📝grid-start, grid-end, grid-column, grid-row
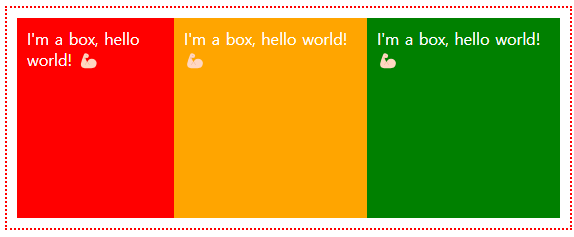
<div class="father">
<div class="child">1</div>
<div class="child">2</div>
<div class="child">3</div>
<div class="child">4</div>
</div>
.father {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 100px 200px 50px;
grid-template-rows: 200px 100px;
row-gap: 10px;
column-gap: 20px;
}
.child {
background-color: tomato;
display: flex;
color: white;
font-size: 28px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.child:last-child {
background-color: turquoise;
/* grid-column-start: 2;
grid-column-end: -1; */
grid-column: 2 / -1;
}
.child:first-child {
/* grid-row-start: 1;
grid-row-end: -1; */
grid-row: 1 / -1;
}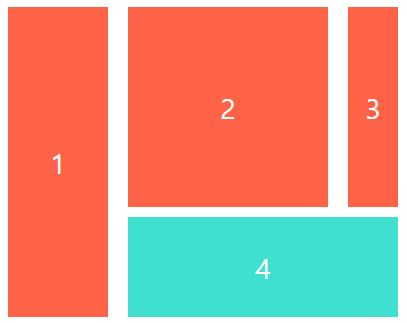
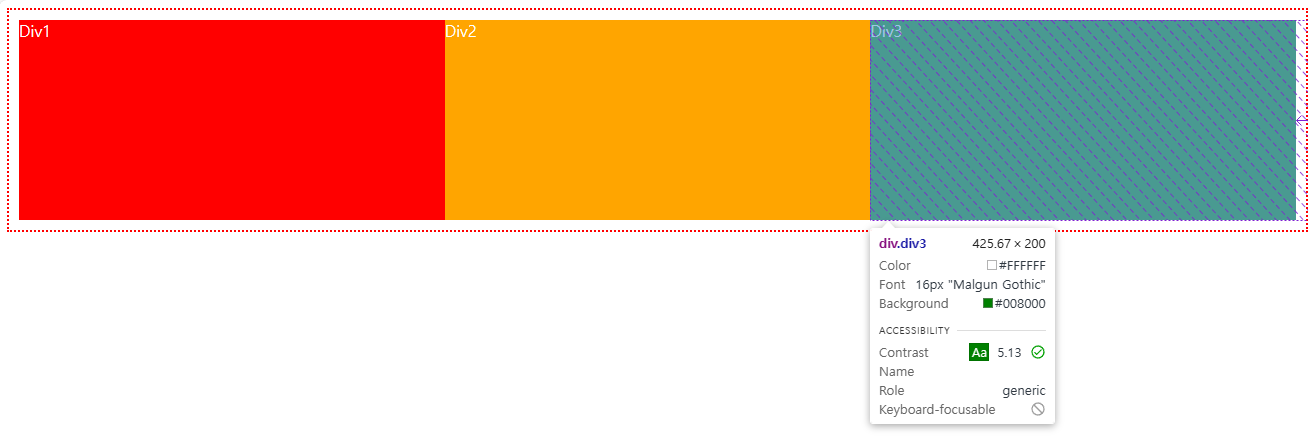
grid-column-start는 어디서 시작을 의미하고 grid-column-end는 어디까지 차지할지에 대해서 의미합니다. grid-column을 통해 한번에 설정도 가능합니다. (grid-column-start가 2이면 2번째열에서 -1인 마지막열까지 차지하겠다는 의미)
grid-row의 경우는 행에 대해 시작지점과 종료시점을 지정하는 것이 동일합니다
📝span
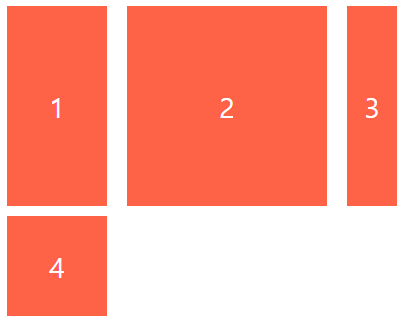
<div class="father">
<div class="child">1</div>
<div class="child">2</div>
<div class="child">3</div>
<div class="child">4</div>
</div>
.father {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 100px 200px 50px 50px;
grid-template-rows: 200px 100px ;
row-gap: 10px;
column-gap: 20px;
}
.child {
background-color: tomato;
display: flex;
color: white;
font-size: 28px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.child:last-child {
background-color: turquoise;
/* grid-column-start: 2;
grid-column-end: -1; */
grid-column: 2 / span 3;
}
.child:first-child {
/* grid-row-start: 1;
grid-row-end: -1; */
grid-row: 1 / -1;
}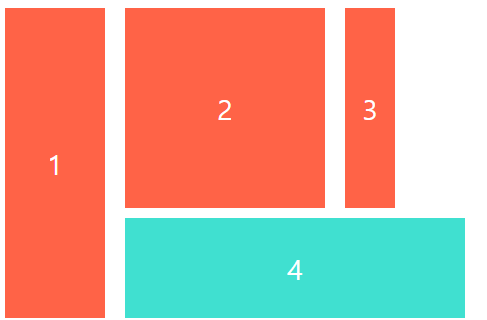
span은 grid-colum-start로 시작지점을 잡고 종료지점을 정하는게 아닌 몇개까지 차지하겠다라는 걸 표시해줄 수 있습니다. 위 코드를 보면 grid-column의 start는 2번째 열이고 2번째열을 포함한 3개까지 차지하겠다는 의미입니다.
📝place-items, place-self
<div class="father">
<div class="child">1</div>
<div class="child">2</div>
<div class="child">3</div>
<div class="child">4</div>
<div class="child">5</div>
<div class="child">6</div>
<div class="child">7</div>
<div class="child">8</div>
<div class="child">9</div>
<div class="child">10</div>
</div>
.father {
display: grid;
gap: 10px;
min-height: 50vh;
grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr);
grid-template-rows: repeat(2, 1fr);
grid-auto-rows: 1fr;
grid-auto-columns: 1fr;
grid-auto-flow: column;
place-items: end center;
}
.child {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
font-size: 28px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.child:nth-child(6) {
background-color: teal;
/* align-self: start;
justify-self: end; */
place-self: center center;
grid-column: span 2;
}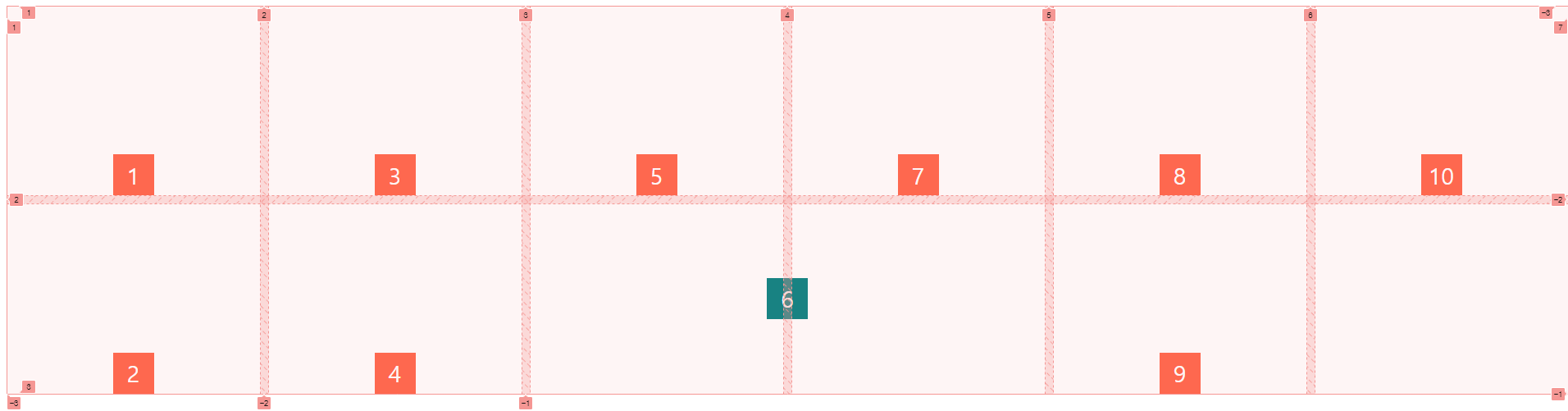
place-items의 경우 부모에 적용시키며 전체 grid안에 있는 contents를 정렬을 해줍니다. 앞에 나오는 건 행에 대한 정렬 뒤에 나오는 건 열에 대한 정렬입니다. (end center)
place-self는 부모 전체가 아니라 개별로 자식에 적용시키며 해당 grid의 상하좌우 정렬을 해줍니다.
📝justifiy-content, align-content, place-content
<div class="father">
<div class="child">1</div>
<div class="child">2</div>
<div class="child">3</div>
<div class="child">4</div>
<div class="child">5</div>
<div class="child">6</div>
<div class="child">7</div>
<div class="child">8</div>
<div class="child">9</div>
<div class="child">10</div>
</div>
.father {
display: grid;
gap: 10px;
height: 100vh;
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 100px);
grid-template-rows: repeat(2, 100px);
background-color: lightblue;
/*justify-content: center;*/
/*align-content: center;*/
place-content: center center;
}
.child {
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
font-size: 28px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}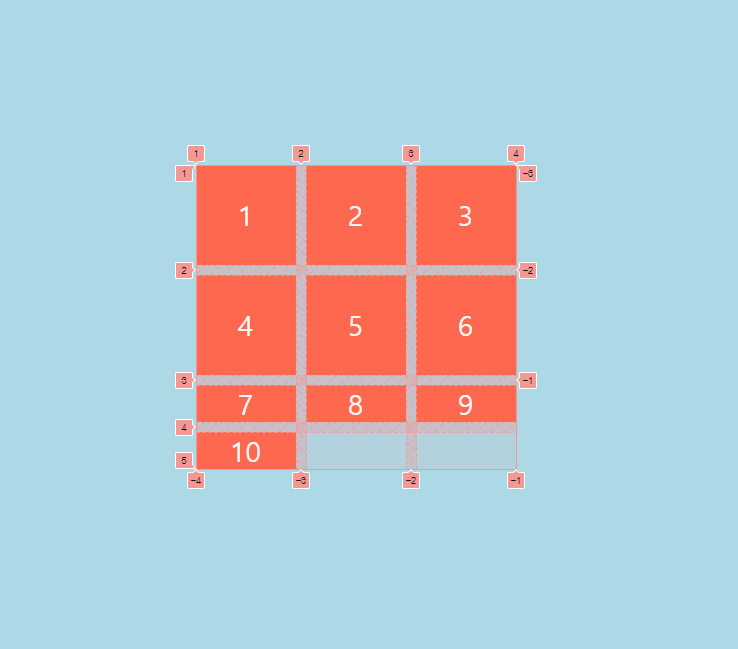
place-items, place-self의 경우는 grid안에서의 정렬이지만 flexbox처럼 전체에 대한 정렬의 경우는 좌우 정렬인 justify-content하고 상하 정렬인 align-content를 사용합니다. (place-content로 축약해서 상하좌우 정렬을 입력할 수 있습니다)
📝minmax
<div class="father">
<div class="child">1fr</div>
<div class="child">1fr</div>
<div class="child">1fr</div>
</div>
.father {
display: grid;
gap: 10px;
height: 100vh;
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, minmax(200px, 400px));
}
.child {
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
font-size: 50px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
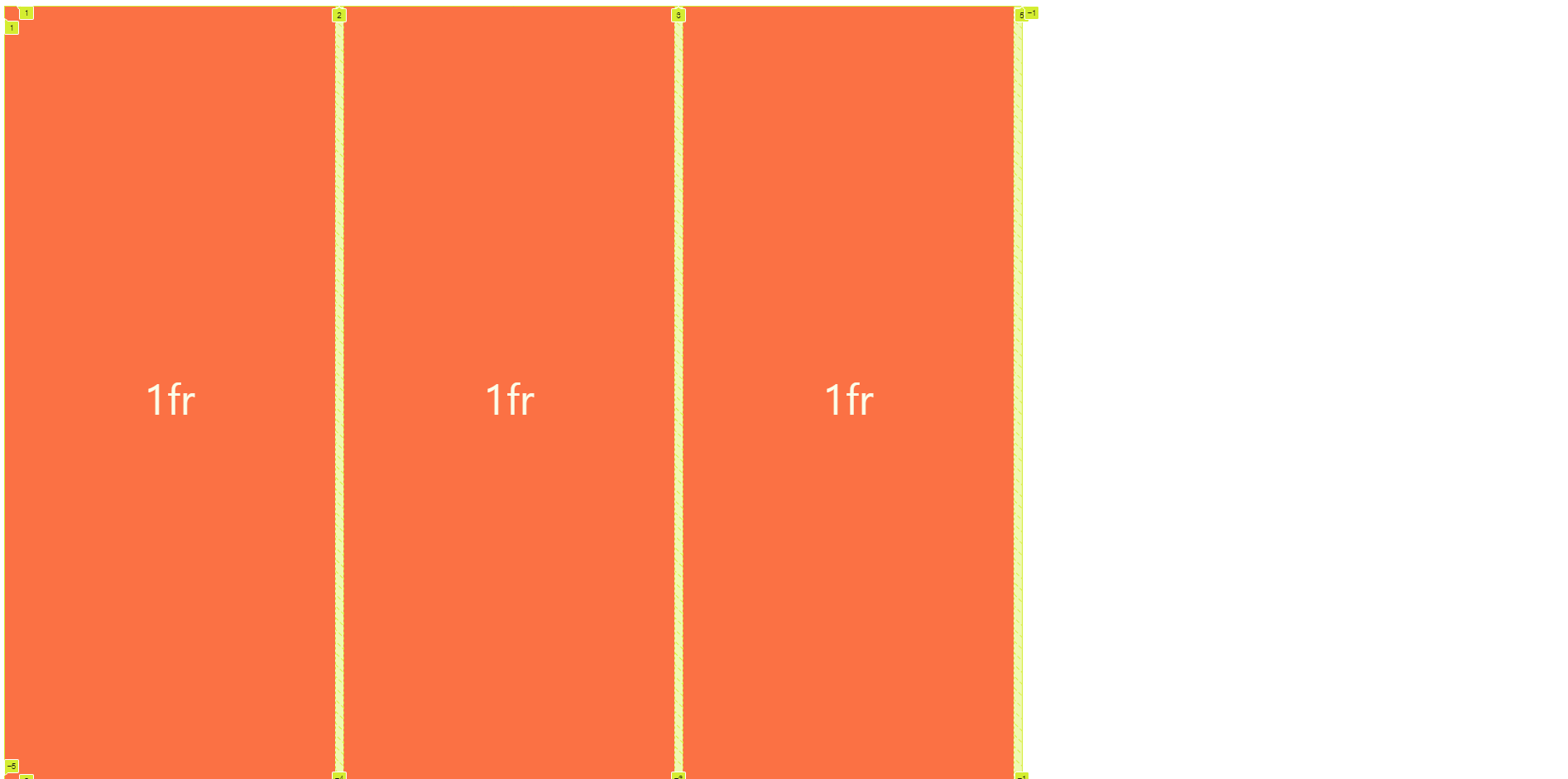
}minmax의 경우 grid 한개당 최소 크기 최대크기를 설정할 수 있습니다
📝auto-fit, auto-fill (반응형)
<div class="father">
<div class="child">1fr</div>
<div class="child">1fr</div>
<div class="child">1fr</div>
</div>
.father {
display: grid;
gap: 10px;
height: 100vh;
grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fill, minmax(200px, 400px));
/*grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fit, minmax(200px, 400px));*/
}
.child {
background-color: tomato;
color: white;
font-size: 50px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
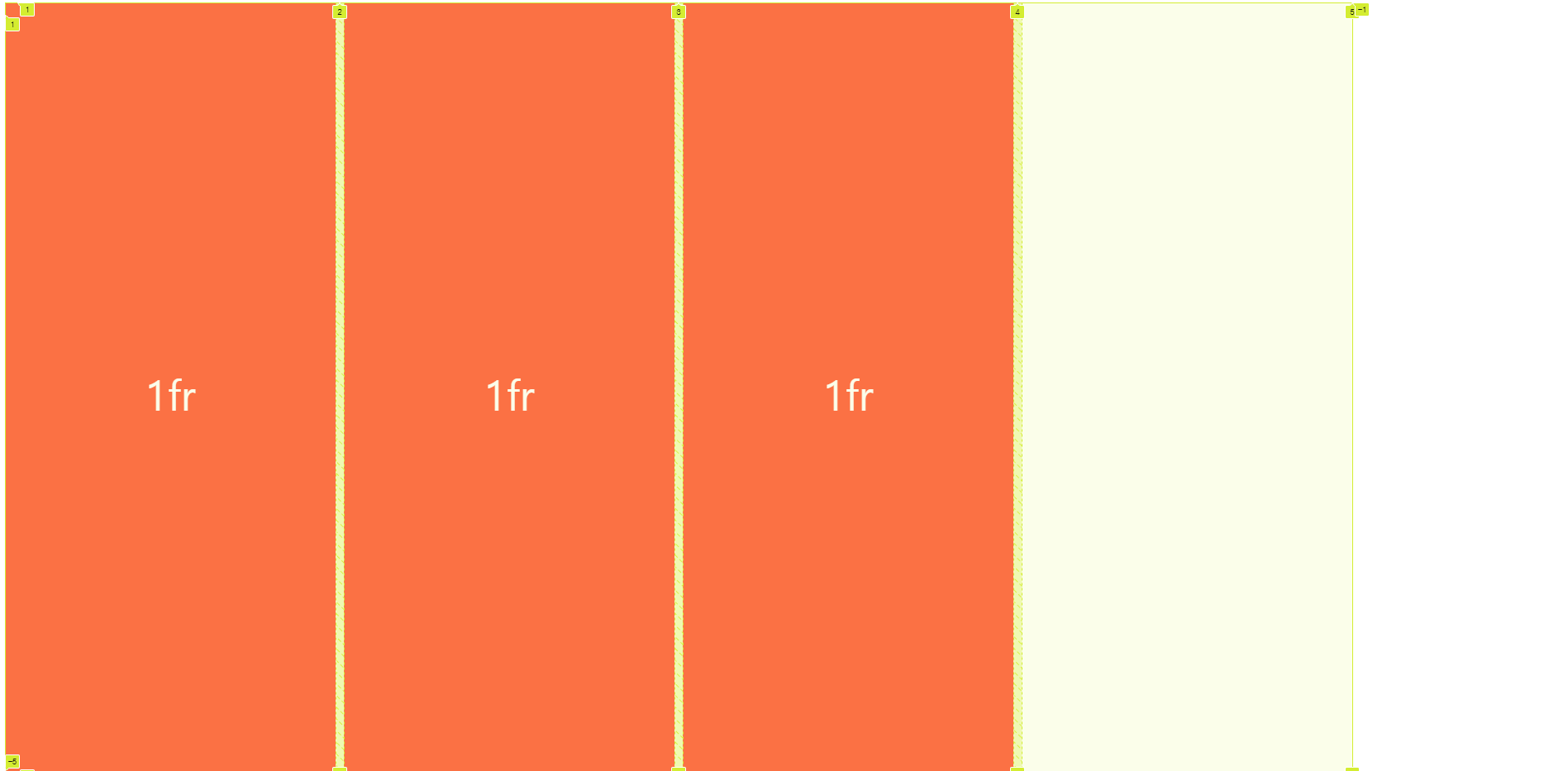
auto-fit의 경우는 HTML에 있는 자식 개수만큼만 딱 채웁니다.
auto-fill의 경우 HTML에 있는 자식 개수만큼 그리지만 max크기만큼 더 그릴 수 있을 때는 그만큼 자리를 차지합니다.
공통점으로 둘다 화면크기를 줄였을 때 max크기에 맞춰서 반응형처럼 바뀝니다.