📝useState (상태 관리)
function MyButton() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
function handleClick() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
return (
<button onClick={handleClick}>
Clicked {count} times
</button>
);
}리액트는 필요한 부분만 렌더링하기 위한 리액트만의 방식이 있습니다 useState라는 걸 이용해 값을 저장하고 그 값이 Setter로 변화시켰을 때 감지해 그 부분만 렌더링시키게 합니다
가장 많이 사용하는 것이라 필수적으로 익혀둬야합니다
- 조건문, 반복문 또는 기타 중첩 함수 내부에서는 훅을 호출할 수 없습니다
- 명명 규칙으로는 명사를 따르며 set + State변수명으로 setter 함수를 만드시면 됩니다
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-ryf69v?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-ryf69v?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
codesandbox.io
state가 서로 독립적이기 때문에 개별적으로 돌아갑니다
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-5rx42k?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-5rx42k?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
codesandbox.io
📝useState (객체, 배열)
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Form() {
const [person, setPerson] = useState({
firstName: 'Barbara',
lastName: 'Hepworth',
email: 'bhepworth@sculpture.com'
});
function handleFirstNameChange(e) {
setPerson({
...person,
firstName: e.target.value
});
}
function handleLastNameChange(e) {
setPerson({
...person,
lastName: e.target.value
});
}
function handleEmailChange(e) {
setPerson({
...person,
email: e.target.value
});
}
return (
<>
<label>
First name:
<input
value={person.firstName}
onChange={handleFirstNameChange}
/>
</label>
<label>
Last name:
<input
value={person.lastName}
onChange={handleLastNameChange}
/>
</label>
<label>
Email:
<input
value={person.email}
onChange={handleEmailChange}
/>
</label>
<p>
{person.firstName}{' '}
{person.lastName}{' '}
({person.email})
</p>
</>
);
}state에 저장한 자바스크립트 객체와 배열은 어떤 것이라도 읽기 전용인 것처럼 다루어야 합니다
렌더링시 상태 값에 변화를 주려면 setState에 새로운 객체 및 배열을 할당해줘야하고 ...로 기존 데이터를 유지시키며 다른 데이터를 덮어씌워서 변화를 줄 수 있습니다
| 비선호 (배열 변경) | 선호 (새 배열 반환) | |
| 추가 | push, unshift | concat, [...arr] 전개 연산자 |
| 제거 | pop, shift, splice | filter, slice |
| 교체 | splice, arr[i] = 값 할당 | map |
| 정렬 | reverse, sort | 배열 복사한 이후에 처리 |
React에서 선호하는 방식으로 배열 함수를 사용해서 새로운 배열을 만들어서 setState에 할당해주면 됩니다
📝useState 동작과정
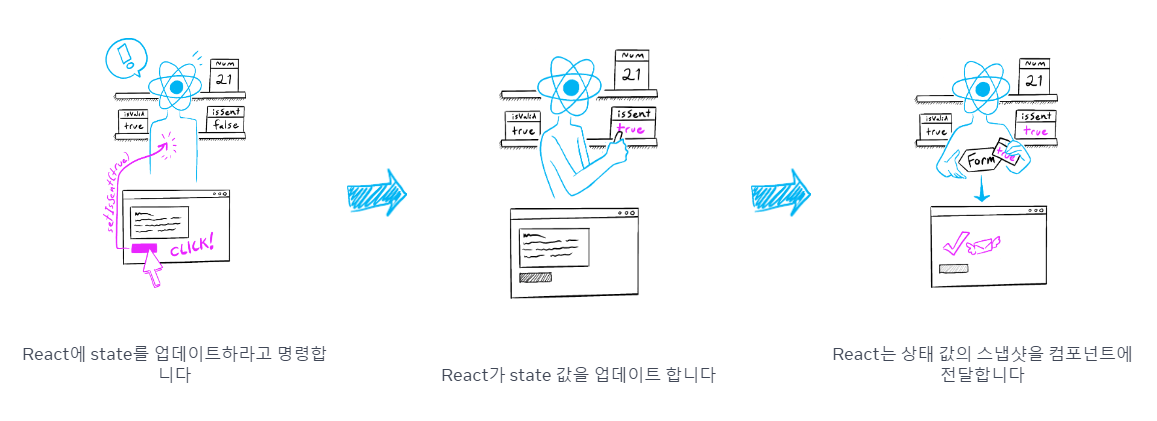
state 변화가 일어날 때 스냅샷을 만든 다음 state 변화에 대한 내용을 작성합니다 그 이후 현재 화면과 스냅샷 화면을 비교해서 해당 부분만 업데이트합니다
export default function Counter() {
const [number, setNumber] = useState(0);
return (
<>
<h1>{number}</h1>
<button onClick={() => {
setNumber(number + 1);
setNumber(number + 1);
setNumber(number + 1);
}}>+3</button>
</>
)
}
/** 첫번째 클릭 **/
<button onClick={() => {
setNumber(0 + 1);
setNumber(0 + 1);
setNumber(0 + 1);
}}>+3</button>
/** 두번째 클릭 **/
<button onClick={() => {
setNumber(1 + 1);
setNumber(1 + 1);
setNumber(1 + 1);
}}>+3</button>위코드를 실행시킬 경우 +3이 아니라 가장 마지막에 있는 변화만 적용시킵니다 그래서 1이 보이게 됩니다
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/s/ffhp6h?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
react.dev - CodeSandbox
react.dev using react, react-dom, react-scripts
codesandbox.io
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Counter() {
const [number, setNumber] = useState(0);
return (
<>
<h1>{number}</h1>
<button onClick={() => {
setNumber(number + 5);
setTimeout(() => {
alert(number);
}, 3000);
}}>+5</button>
</>
)시간의 경과가 있어도 동일하게 작동합니다
요약하자면 처음 클릭할 때 state는 유지되고 그 context가 있기 때문에 3초가 지나도 alert에도 0이 찍히게 되고 렌더링 한 이후에는 state가 바뀌게 되고 서로 다른 context가 존재하기 때문에 서로 간섭 안 해서 사이드이펙트가 일어나지 않습니다
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/s/sz392q?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
react.dev - CodeSandbox
react.dev using react, react-dom, react-scripts
codesandbox.io
📝같은 자리의 컴포넌트 state 보존 (state 특징)
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function App() {
const [isFancy, setIsFancy] = useState(false);
return (
<div>
{isFancy ? (
<Counter isFancy={true} />
) : (
<Counter isFancy={false} />
)}
<label>
<input
type="checkbox"
checked={isFancy}
onChange={e => {
setIsFancy(e.target.checked)
}}
/>
Use fancy styling
</label>
</div>
);
}
function Counter({ isFancy }) {
const [score, setScore] = useState(0);
const [hover, setHover] = useState(false);
let className = 'counter';
if (hover) {
className += ' hover';
}
if (isFancy) {
className += ' fancy';
}
return (
<div
className={className}
onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)}
onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)}
>
<h1>{score}</h1>
<button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}>
Add one
</button>
</div>
);
}여기서 삼항연산자로 true일경우 <Counter isFancy={true}/> false일 경우 <Counter isFancy={false}/>을 보여주는데 체크박스로 isFancy값을 변경시켜도 Counter에 있는 count값은 변화하지 않는데 같은 자리의 같은 컴포넌트는 state를 보존합니다

예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/s/6f2zp8?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
react.dev - CodeSandbox
react.dev using react, react-dom, react-scripts
codesandbox.io
📝같은 자리의 컴포넌트 state 보존 안 시키기 (state 특징)
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Scoreboard() {
const [isPlayerA, setIsPlayerA] = useState(true);
return (
<div>
{isPlayerA &&
<Counter person="Taylor" />
}
{!isPlayerA &&
<Counter person="Sarah" />
}
<button onClick={() => {
setIsPlayerA(!isPlayerA);
}}>
Next player!
</button>
</div>
);
}
function Counter({ person }) {
const [score, setScore] = useState(0);
const [hover, setHover] = useState(false);
let className = 'counter';
if (hover) {
className += ' hover';
}
return (
<div
className={className}
onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)}
onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)}
>
<h1>{person}'s score: {score}</h1>
<button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}>
Add one
</button>
</div>
);
}이건 위에 코드랑 비슷해보이지만 삼항연산자로 되어있는게 아니라서 위치가 바뀌기 때문에 state가 유지가 안 됩니다

예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/s/g9f9r8?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
react.dev - CodeSandbox
react.dev using react, react-dom, react-scripts
codesandbox.io
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Scoreboard() {
const [isPlayerA, setIsPlayerA] = useState(true);
return (
<div>
{isPlayerA ? (
<Counter key="Taylor" person="Taylor" />
) : (
<Counter key="Sarah" person="Sarah" />
)}
<button onClick={() => {
setIsPlayerA(!isPlayerA);
}}>
Next player!
</button>
</div>
);
}
function Counter({ person }) {
const [score, setScore] = useState(0);
const [hover, setHover] = useState(false);
let className = 'counter';
if (hover) {
className += ' hover';
}
return (
<div
className={className}
onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)}
onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)}
>
<h1>{person}'s score: {score}</h1>
<button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}>
Add one
</button>
</div>
);
}key를 주게 되면 위치로 판단하는게 아니라 key로 찾아가기 때문에 삼항연산자를 써도 state가 초기화됩니다
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-wvssxq?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-wvssxq?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
codesandbox.io
📝렌더링 전에 동일 state 변수 여러번 업데이트
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Counter() {
const [number, setNumber] = useState(0);
return (
<>
<h1>{number}</h1>
<button onClick={() => {
setNumber(n => n + 1);
setNumber(n => n + 15);
setNumber(n => n + 10);
}}>+N</button>
</>
)
}흔한 사례는 아니지만 만약 동일한 Context내에서 state 변수를 여러번 업데이트 하려면 위와 같이 사용하면 됩니다
여기서 n은 변화된 값을 가지고 있는 변수라고 생각하시면 됩니다 그렇기 때문에 원래라면 10이 보여야하지만 1+15+10을 다 더한 26이 보이게 됩니다
📝연관된 state 그룹화 (React State 팁)
/** 변경전 **/
const [x, setX] = useState(0);
const [y, setY] = useState(0);
/** 변경후 **/
const [position, setPosition] = useState({ x: 0, y: 0 });두 개의 state 변수가 항상 함께 변경된다면, 단일 state 변수로 통합하는 것이 좋습니다
📝state 중복 피하기 (React State 팁)
import { useState } from 'react';
const initialItems = [
{ title: 'pretzels', id: 0 },
{ title: 'crispy seaweed', id: 1 },
{ title: 'granola bar', id: 2 },
];
export default function Menu() {
const [items, setItems] = useState(initialItems);
const [selectedItem, setSelectedItem] = useState(
items[0]
);
function handleItemChange(id, e) {
setItems(items.map(item => {
if (item.id === id) {
return {
...item,
title: e.target.value,
};
} else {
return item;
}
}));
}
return (
<>
<h2>What's your travel snack?</h2>
<ul>
{items.map((item, index) => (
<li key={item.id}>
<input
value={item.title}
onChange={e => {
handleItemChange(item.id, e)
}}
/>
{' '}
<button onClick={() => {
setSelectedItem(item);
}}>Choose</button>
</li>
))}
</ul>
<p>You picked {selectedItem.title}.</p>
</>
);
}현재는 선택된 항목을 selectedItem state 변수에 객체로 저장합니다. 그러나 이는 좋지 않습니다. selectedItem의 내용이 items 목록 내의 항목 중 하나와 동일한 객체입니다. 이는 항목 자체에 대한 정보가 두 곳에서 중복되는 것입니다
“Choose”를 클릭한 후 이를 편집할 경우, 입력이 업데이트되지만, 하단의 라벨에는 편집 내용이 반영되지 않습니다
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/s/qwm2gy?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
react.dev - CodeSandbox
react.dev using react, react-dom, react-scripts
codesandbox.io
import { useState } from 'react';
const initialItems = [
{ title: 'pretzels', id: 0 },
{ title: 'crispy seaweed', id: 1 },
{ title: 'granola bar', id: 2 },
];
export default function Menu() {
const [items, setItems] = useState(initialItems);
const [selectedId, setSelectedId] = useState(0);
const selectedItem = items.find(item =>
item.id === selectedId
);
function handleItemChange(id, e) {
setItems(items.map(item => {
if (item.id === id) {
return {
...item,
title: e.target.value,
};
} else {
return item;
}
}));
}
return (
<>
<h2>What's your travel snack?</h2>
<ul>
{items.map((item, index) => (
<li key={item.id}>
<input
value={item.title}
onChange={e => {
handleItemChange(item.id, e)
}}
/>
{' '}
<button onClick={() => {
setSelectedId(item.id);
}}>Choose</button>
</li>
))}
</ul>
<p>You picked {selectedItem.title}.</p>
</>
);
}selectedItem을 selectedItemId로 변경하고 id값으로 item을 찾으면 item이 변경되어도 똑같이 변경되게 되는 것이죠
예제 코드 (개선)
https://codesandbox.io/s/8mhwpl?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
react.dev - CodeSandbox
react.dev using react, react-dom, react-scripts
codesandbox.io
📝깊게 중첩된 state 피하기 (React State 팁)
export const initialTravelPlan = {
id: 0,
title: '(Root)',
childPlaces: [{
id: 1,
title: 'Earth',
childPlaces: [{
id: 2,
title: 'Africa',
childPlaces: [{
id: 3,
title: 'Botswana',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 4,
title: 'Egypt',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 5,
title: 'Kenya',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 6,
title: 'Madagascar',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 7,
title: 'Morocco',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 8,
title: 'Nigeria',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 9,
title: 'South Africa',
childPlaces: []
}]
}, {
id: 10,
title: 'Americas',
childPlaces: [{
id: 11,
title: 'Argentina',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 12,
title: 'Brazil',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 13,
title: 'Barbados',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 14,
title: 'Canada',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 15,
title: 'Jamaica',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 16,
title: 'Mexico',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 17,
title: 'Trinidad and Tobago',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 18,
title: 'Venezuela',
childPlaces: []
}]
}, {
id: 19,
title: 'Asia',
childPlaces: [{
id: 20,
title: 'China',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 21,
title: 'India',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 22,
title: 'Singapore',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 23,
title: 'South Korea',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 24,
title: 'Thailand',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 25,
title: 'Vietnam',
childPlaces: []
}]
}, {
id: 26,
title: 'Europe',
childPlaces: [{
id: 27,
title: 'Croatia',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 28,
title: 'France',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 29,
title: 'Germany',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 30,
title: 'Italy',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 31,
title: 'Portugal',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 32,
title: 'Spain',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 33,
title: 'Turkey',
childPlaces: [],
}]
}, {
id: 34,
title: 'Oceania',
childPlaces: [{
id: 35,
title: 'Australia',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 36,
title: 'Bora Bora (French Polynesia)',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 37,
title: 'Easter Island (Chile)',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 38,
title: 'Fiji',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 39,
title: 'Hawaii (the USA)',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 40,
title: 'New Zealand',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 41,
title: 'Vanuatu',
childPlaces: [],
}]
}]
}, {
id: 42,
title: 'Moon',
childPlaces: [{
id: 43,
title: 'Rheita',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 44,
title: 'Piccolomini',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 45,
title: 'Tycho',
childPlaces: []
}]
}, {
id: 46,
title: 'Mars',
childPlaces: [{
id: 47,
title: 'Corn Town',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 48,
title: 'Green Hill',
childPlaces: []
}]
}]
};만일 state가 쉽게 업데이트하기에 너무 중첩되어 있다면, “평탄”하게 만드는 것을 고려하세요
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/s/vmm64f?file=%2Fsrc%2Fplaces.js&utm_medium=sandpack
react.dev - CodeSandbox
react.dev using react, react-dom, react-scripts
codesandbox.io
개선된 코드
export const initialTravelPlan = {
0: {
id: 0,
title: '(Root)',
childIds: [1, 42, 46],
},
1: {
id: 1,
title: 'Earth',
childIds: [2, 10, 19, 26, 34]
},
2: {
id: 2,
title: 'Africa',
childIds: [3, 4, 5, 6 , 7, 8, 9]
},
3: {
id: 3,
title: 'Botswana',
childIds: []
},
4: {
id: 4,
title: 'Egypt',
childIds: []
},
5: {
id: 5,
title: 'Kenya',
childIds: []
},
6: {
id: 6,
title: 'Madagascar',
childIds: []
},
7: {
id: 7,
title: 'Morocco',
childIds: []
},
8: {
id: 8,
title: 'Nigeria',
childIds: []
},
9: {
id: 9,
title: 'South Africa',
childIds: []
},
10: {
id: 10,
title: 'Americas',
childIds: [11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18],
},
11: {
id: 11,
title: 'Argentina',
childIds: []
},
12: {
id: 12,
title: 'Brazil',
childIds: []
},
13: {
id: 13,
title: 'Barbados',
childIds: []
},
14: {
id: 14,
title: 'Canada',
childIds: []
},
15: {
id: 15,
title: 'Jamaica',
childIds: []
},
16: {
id: 16,
title: 'Mexico',
childIds: []
},
17: {
id: 17,
title: 'Trinidad and Tobago',
childIds: []
},
18: {
id: 18,
title: 'Venezuela',
childIds: []
},
19: {
id: 19,
title: 'Asia',
childIds: [20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25],
},
20: {
id: 20,
title: 'China',
childIds: []
},
21: {
id: 21,
title: 'India',
childIds: []
},
22: {
id: 22,
title: 'Singapore',
childIds: []
},
23: {
id: 23,
title: 'South Korea',
childIds: []
},
24: {
id: 24,
title: 'Thailand',
childIds: []
},
25: {
id: 25,
title: 'Vietnam',
childIds: []
},
26: {
id: 26,
title: 'Europe',
childIds: [27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33],
},
27: {
id: 27,
title: 'Croatia',
childIds: []
},
28: {
id: 28,
title: 'France',
childIds: []
},
29: {
id: 29,
title: 'Germany',
childIds: []
},
30: {
id: 30,
title: 'Italy',
childIds: []
},
31: {
id: 31,
title: 'Portugal',
childIds: []
},
32: {
id: 32,
title: 'Spain',
childIds: []
},
33: {
id: 33,
title: 'Turkey',
childIds: []
},
34: {
id: 34,
title: 'Oceania',
childIds: [35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41],
},
35: {
id: 35,
title: 'Australia',
childIds: []
},
36: {
id: 36,
title: 'Bora Bora (French Polynesia)',
childIds: []
},
37: {
id: 37,
title: 'Easter Island (Chile)',
childIds: []
},
38: {
id: 38,
title: 'Fiji',
childIds: []
},
39: {
id: 40,
title: 'Hawaii (the USA)',
childIds: []
},
40: {
id: 40,
title: 'New Zealand',
childIds: []
},
41: {
id: 41,
title: 'Vanuatu',
childIds: []
},
42: {
id: 42,
title: 'Moon',
childIds: [43, 44, 45]
},
43: {
id: 43,
title: 'Rheita',
childIds: []
},
44: {
id: 44,
title: 'Piccolomini',
childIds: []
},
45: {
id: 45,
title: 'Tycho',
childIds: []
},
46: {
id: 46,
title: 'Mars',
childIds: [47, 48]
},
47: {
id: 47,
title: 'Corn Town',
childIds: []
},
48: {
id: 48,
title: 'Green Hill',
childIds: []
}
};
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-q63dwl?file=%2Fsrc%2Fplaces.js&utm_medium=sandpack
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-q63dwl?file=%2Fsrc%2Fplaces.js&utm_medium=sandpack
codesandbox.io
📝Props (데이터 전달)
export default function MyApp() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
function handleClick() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
return (
<div>
<h1>Counters that update together</h1>
<MyButton count={count} onClick={()=>handleClick()} />
<MyButton count={count} onClick={handleClick} />
{/* 잘못된 전달 <MyButton count={count} onClick={handleClick()} /> */}
</div>
);
}
function MyButton({ count, onClick }) {
return (
<button onClick={onClick}>
Clicked {count} times
</button>
);
}부모에서 자식 컴포넌트에 값을 전달하기위해 파라미터처럼 값을 보내줘야하는데 이러한 인자값 정의를 Props라고합니
다 (Property를 보낸다라는 느낌)
JSX에서 작성된 Props는 JavaScript 객체의 키가 됩니다 그래서 변수명에 대시를 포함하거나 class처럼 예약어를 사용할 수 없습니다 그래서 대부분 camelCase를 사용합니다
React는 {} 중괄호에 있는 건 다 실행시킵니다 그렇기 때문에 함수() 이런식으로 넣는 경우 바로 동작하게 됩니다
Props처럼 컴포넌트에 매개변수를 넣어줄 수 있는데 함수를 넘길 경우 ()라는 실행한 값이 아닌 함수의 참조값이나 익명함수를 전달해줘야합니다
예제 코드
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-jmpn67?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
https://codesandbox.io/p/sandbox/react-dev-jmpn67?file=%2Fsrc%2FApp.js&utm_medium=sandpack
codesandbox.io
📝Props 기본값 설정
function Avatar({ person, size = 100 }) {
// ...
}위 코드처럼 기본값 설정할 수 있습니다
📝Props 팁
function Profile({ person, size, isSepia, thickBorder }) {
return (
<div className="card">
<Avatar
person={person}
size={size}
isSepia={isSepia}
thickBorder={thickBorder}
/>
</div>
);
}
function Profile(props) {
return (
<div className="card">
<Avatar {...props} />
</div>
);
}위 코드와 같이 props의 키와 값을 동일하게 설정하면 코드를 간결화할 수 있습니다
... spread 문법은 많이 사용하기 때문에 익숙해지길 바랍니다
export default function StoryTray({ stories }) {
stories.push({
id: 'create',
label: 'Create Story'
});
return (
<ul>
{stories.map(story => (
<li key={story.id}>
{story.label}
</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}props로 받는 데이터는 그 자체를 변형시켜서는 안 됩니다
📝자식을 JSX로 전달 (children)
/** HTML 방식 **/
<div>
<img />
</div>
/** React 방식 **/
<Card>
<Avatar />
</Card>컴포넌트를 중첩해서 쓰고 싶을 때가 있습니다 children을 사용하면 이를 쉽게 사용할 수있습니다
import Avatar from './Avatar.js';
function Card({ children }) {
return (
<div className="card">
{children}
</div>
);
}
export default function Profile() {
return (
<Card>
<Avatar
size={100}
person={{
name: 'Katsuko Saruhashi',
imageId: 'YfeOqp2'
}}
/>
</Card>
);
}Card 컴포넌트 안에 들어가는 하위 것들을 children으로 퉁쳐서 들어갈 수 있습니다